Design Manual (M22-01), Chapter 1010 - Work Zone Safety and Mobility (PDF 455KB)
Traffic Manual (M51-02), Chapter 5 - Work Zone Traffic Control (PDF 3.3MB)
Work Zone Traffic Control Guidelines for Maintenance Operations (M54-44)
Division 2 - Temporary Features (PDF 420KB)
Section 2-04 - Temporary Traffic Control
(Note: This was previously Section 1-10 in the Standard Specifications before the 2026 edition)
Division 8 - Miscellaneous Construction (PDF 1.1MB)
Section 8-23 - Temporary Pavement Markings
Division 9 - Materials (PDF 1.9MB)
Section 9-35 - Temporary Traffic Control Materials
General Special Provisions (GSPs)
Division 1 - General Requirements (PDF 469KB)
Section 1-10 - Temporary Traffic Control (Includes Section 9-35 items)
Traffic Management Plans
A TMP is a set of strategies to manage the work zone mobility and safety impacts of a project. TMP development begins in scoping by assessing various Work Zone Traffic Control strategies, evaluating their expected impacts, and selecting mitigation strategies and design solutions to manage those impacts. It is very important to update the TMP through the project development process. See Design Manual Chapter 1010.03 for more information on TMPs and when they are required. At a minimum, Traffic Control Plans and Contract Provisions are required for all projects.
Example Traffic Management Plans
- Eastern Region Chip Seal (PDF 540KB)
- Eastern Region Bridge Special Repairs - SR 26 US 195 (PDF 5MB)
- I-5 Seattle Concrete Rehabilitation (PDF 186KB)
- I-5 Cowlitz River Bridge - Repair Bridge (PDF 1MB)
- I-90 Spokane Special Bridge Repair (PDF 98KB)
- I-405 - SR 167 Interchange Connector Project (PDF 172KB)
- I-405 Hard Shoulder Running (PDF 183KB)
- SR 20 Jefferson County Culvert Replacement (PDF 136KB)
Smart Work Zone Systems
Queue detection & mitigation
A Smart Work Zone System and Queue Warning Systems read traffic speeds by using portable sensors leading onto a lane closure or restriction. Data from these sensors trigger message changes on signs before the work zone. The signs inform drivers of the presence and location of slowed or backed up traffic before they see brake lights.
These systems optimize the safety and efficiency of traffic through the work zone and should be used when queuing is expected to exceed two miles. SWZs can provide information such as queue detection for “slowed or stopped traffic ahead," merging instructions (zipper merging where motorists are instructed to use all open lanes up to the merge point and take turns merging) to reduce the queue lengths, or travel time information so drivers can choose alternate routes.
Connected work zones
Connected work zones that include Temporary Traffic Control Devices that are equipped to transmit work zone activity data like Arrow Boards. This data is made available to publicly accessible navigation applications.
Trucks entering warning system
When haul vehicles need to leave a work zone, they often have to merge with high-speed traffic. Warning signs with beacons can be activated by traffic sensors located in the work zone ahead of the work zone egress locations.

Intersection conflict warning system
When a work zone creates increased traffic movements at an intersection, sensors can be placed to detect the presence of vehicles at the stop bar and on the main line approaching an intersection. Warning signs with beacons can be activated on a side road when mainline traffic is approaching the intersection. Mainline beacons will be activated when traffic is at the intersection or turning through the intersection.
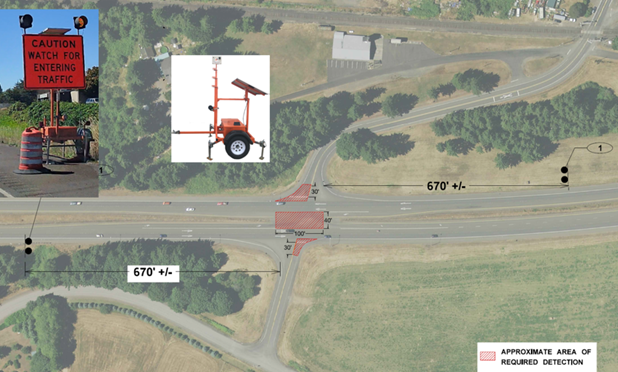
Additional work zone devices
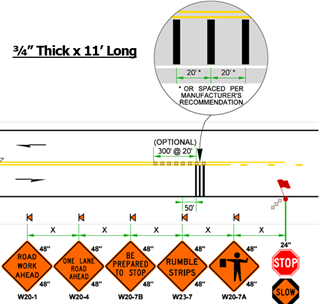
Rumble strips
Temporary Portable Transverse Rumble Strips (TPTRS) provide both an audible warning and physical vibration to alert motorists in addition to warning signs and other temporary traffic control devices as a vehicle approaches a work zone condition. WSDOT recommends the use of TPTRS as an optional countermeasure for flagging operations on roadways 45MPH or higher.
Automated Flagger Assistance Device
Automated Flagger Assistance Device (AFAD) is a portable flagger station device remotely operated by a flagger from a safe location away from traffic, while providing motorists with clear guidance through a temporary traffic control zone.

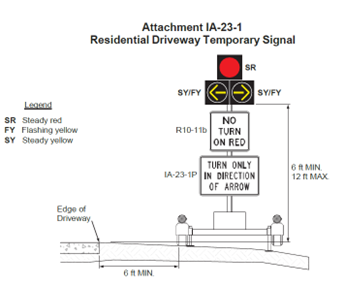
Residential Driveway Temporary Signals
Residential Driveway Temporary Signals (RDTS) are specifically designed for driveways and are used with mainline temporary signals for driveways within the one lane, two-direction segment of the temporary traffic control zone. They inform driveway traffic the direction they are allowed to turn matching the mainline traffic flow directed by the signals.
Radar Speed Display Signs
Radar Speed Display Signs (RDTS) provide feedback to motorists on their current speed and include a speed limit sign of the current roadway speed limit. They are effective in reducing speeds near the device, but higher speeds may resume shortly after motorists pass the device. Locating this device near the active work area is good practice.

Mobile barriers
The mobile barrier system is effective in providing positive protection between workers and traffic for small work areas (< 100 ft.). This barrier system is well-suited for use during bridge joint repairs, pavement patching, manhole adjustments, overhead sign work, and other quick deployment work. Due to its portability, mobile barrier systems can be rapidly deployed to optimize safety and efficiency for projects on high-speed roadways that include multiple small work areas where traditional temporary barriers would not be practical. The Mobile Barriers MBT-1 from Mobile Barriers LLC is currently the only known system that provides this type of similar rapid work zone protection for small work areas and has statewide blanket proprietary item approval.

Moveable barriers
Movable barriers allow for temporary barrier protection that can be moved daily protecting workers on the roadway during active work and moved to the shoulder to maximize lane use for traffic during non-working hours. It is also effective for projects using a median crossover strategy by providing positive separation between opposing traffic and additionally due to its movability, allows daily lane configuration changes to accommodate peak traffic flows.

Smart work zone systems and the other devices listed above can be included on projects by including the appropriate general special provisions (GSPs) and traffic control plans found under the “Standard plans & drawings” or “Specifications” tabs. Trucks entering and intersection conflict warning systems may require modification to smart work zone systems GSP. Please contact us for assistance.
Training
Work Zone Traffic Control (WZTC) Fundamentals & Advanced WZTC Design
This training is open to WSDOT Employees and Consultants and Local Agency Personnel.
The one-day fundamentals class focuses on WZTC basics for design, construction, maintenance and any other WSDOT employees involved with WZTC. The course includes information on traffic control plan selection/development, traffic control devices and their applications, and WZTC policy, guidance and recourses documents.
The one-day advanced course focuses on developing transportation management plans (TMPs) including temporary traffic control plans for long-duration work zones. Temporary barriers, pavement markings, signals, illumination and smart work zone applications will be covered. It is recommended to attend a WZTC Fundamentals course before taking this class.
The target audience for these classes are Transportation Technicians and Transportation Engineers who are responsible for developing traffic control plans. These classes are also beneficial to engineering personnel responsible for construction and implementation of traffic control work zones.
Flagger and Traffic Control Supervisor (TCS) Certification Training
For information on flagging and traffic control supervisor training, see the general Work zone safety page.
WSDOT resources
- WSDOT – Manual of Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD)
- Work Zone Safety
- Work Zone Speed Camera Program
- Work Zone Awareness – Give ‘em a brake. Every year, WSDOT joins DOTs nationwide in recognizing Work Zone Safety Awareness Week, which will take place annually in April. By raising awareness, we aim to protect workers, first responders and travelers on Washington’s roadways. The website includes work zone safety flyers, fact sheet, and work zone safety videos.
- Real-time travel data. View up-to-date travel conditions including travel alerts, cameras, route times, and restrictions.
National work zone resources
- Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD) - Federal Highway Administration
- Work Zone Management Program – The Federal Highway Administration Work Zone Management Program website includes information on many topics including Work Zone Data Exchange (WZDx), ITS & Technology, and worker safety.
- Work Zone Speed Management. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2015.
- National Work Zone Safety Information Clearinghouse
- American Traffic Safety Services Association (ATSSA)
- Connected Work Zone (CWZ) - Institute of Transportation Engineers
WSDOT Traffic Operations - Work Zone Traffic Control
